The skin covers the whole human body and protects it from external damages and infectious diseases. It has different cell types suitably created to adapt our body parts to different functions. The skin over the soles (feet) and palms are specially adapted for rough surfaces and work. However, when we do not take care of our skin properly and protect them from the harsh external environments, it can be damaged. When the genetic material in the cell called the DNA becomes damaged, they can become cancerous. Therefore, an early awareness of any unusual changes is important to detect early cancers and treat them early and correctly before they become serious, larger and spread. As skin cancers advance it will spread to the surrounding areas and finally to the whole body by invading the blood and lymphatic system.
What then are the provoking causes leading to risky or adverse skin changes? The most dangerous factor is the constant exposure to the scorching skin. The sun with the ultra-violet A & B rays are known for its destructive effects on the DNA. With a prolonged exposure to these UV rays the genetic damages progresses and then lead to cancerous changes.
The fairer the skin the more intense is the damages as the UV rays will penetrate deep. Without any blockage by the melanin pigments in the skin, damages will be certain. Those with genetic predisposition like the Albinos or a genetic condition, Xeroderma pigmentosa are definitely prone to the UV damages and prolonged exposure under the sun will certainly lead to multiple skin cancers in due time.
Also, exposure to toxic chemicals like those in the past used in warfare – toxic deforesting agent, radiation, X-rays, ingestion of poisonous chemical like arsenic can cause skin damages. In the construction, painting, manufacturing, mining and agricultural industries there are many toxic chemical compounds used which may contaminate the skin and prolonged exposure may lead to skin damage and possible cancers.
There are 3 common types of skin cancers seen. They are the Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC), Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) and Malignant Melanoma (MM). Others uncommon types are dermatosarcoma, or spread from other cancer sites.
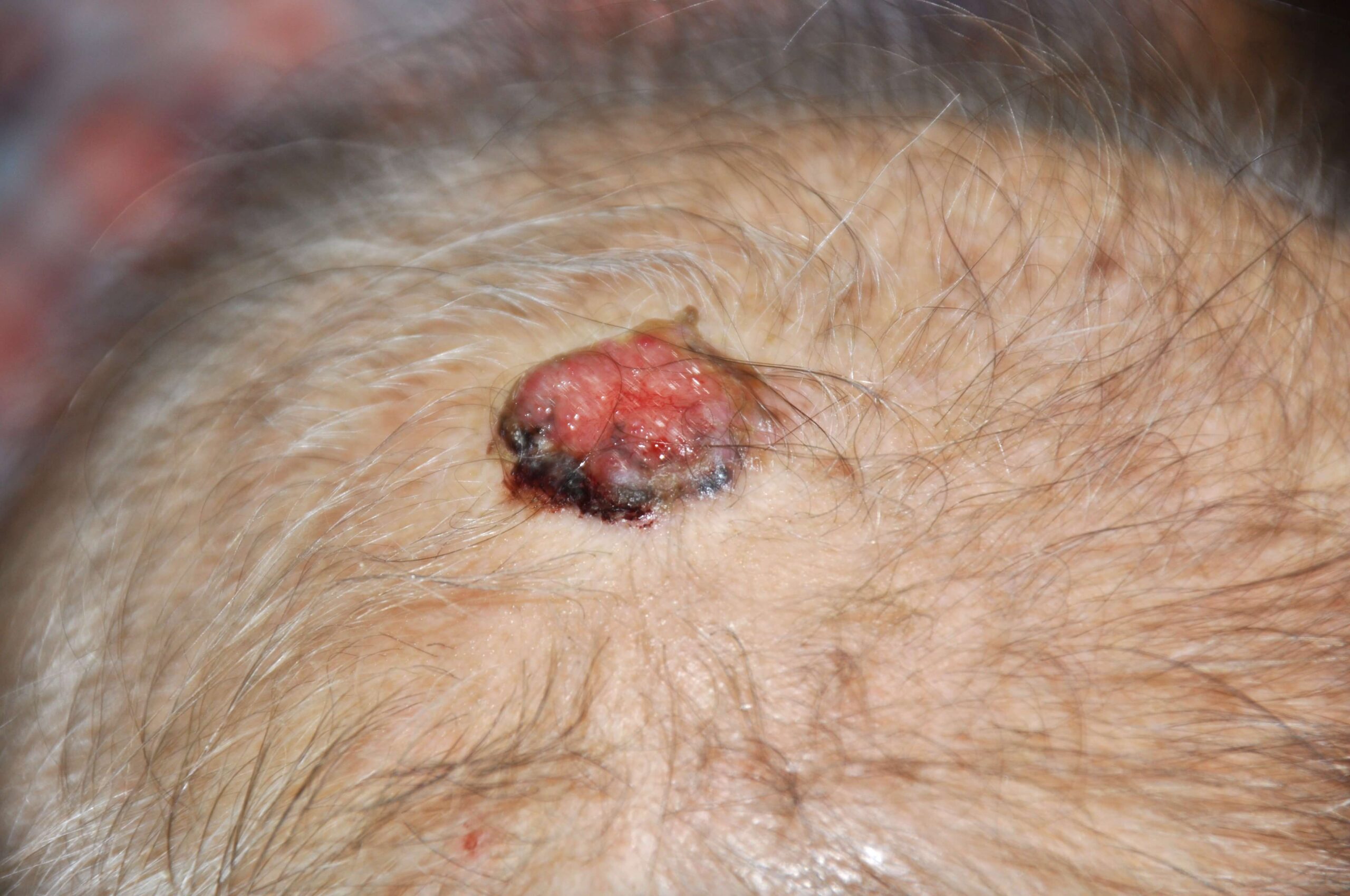
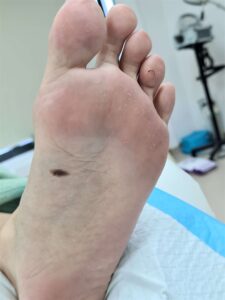
The most important treatment for skin cancers are awareness of changes. One should be aware if existing moles especially the flat irregular black ones suddenly become darker and increasing in size. When those skin lesions suddenly increase in size, becoming itchy and red, forming a hard crust over it, starting to ulcerate or bleeding it should be warning signs to the patients.
(Malignant Melanoma)
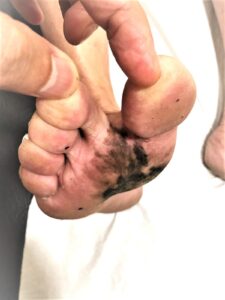
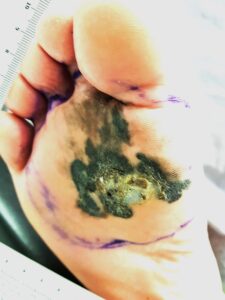
It must be noted that the unusual occurrence of dark pigmented lesions in the sole of the foot, palm, beneath the nail bed or in the mucosa surfaces in the mouth – the red portion of the mouth covering will predispose the patient to the very aggressive malignant melanoma. This skin cancer will spread like wildfire when it invades the lymphatic system, spreading to the regional lymph nodes and then into the whole body. For this cancer, an awareness of this cancer and early complete removal is the treatment of choice before it spreads. The surgery will include an extensive removal of the malignant melanoma, regional block dissection of the lymph nodes if needed when it has spread. This is because all modalities of treatment – radiation therapy, chemotherapy will not control this cancer. Possible experimental use of immunotherapy may offer some hope; but only in the early research stage. Therefore, the prognosis for advanced MM is bleak.
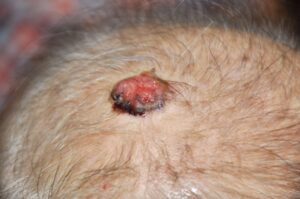
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a slow growing skin cancer which will ulcerate and form a crater-like lesion. There will be bleeding when touched and many small blood vessels around the cancer. BCC is slow growing, but they will infiltrate into the surrounding areas and destroy the structures if left untreated. However, they seldom spread to other parts of the body.
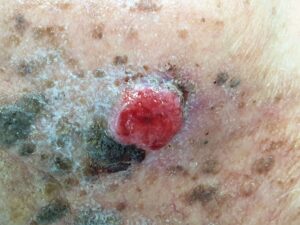
The Squamous Cell Carcinoma can grow fast, ulcerate and bleed from the lesion. After a certain period of time, it will invade the underlying blood and lymphatic system and spread to other parts of the body.
For the treatment of skin cancers, it is important for us to reduce exposure to provoking agent like the scorching sun and toxic chemical compounds. Personal protection like usage of sunblock or sunscreens to reduce the damaging effects of the UV ray or wearing protective hats, clothing and umbrella will reduce exposure to UV rays.
What to do when a skin cancer is suspected? Some will confirm with a biopsy but with a period of possible delay while waiting for the result. But if the lesion is small, a complete removal with good clearance of the surrounding normal skin using the intra-operative frozen section confirmation can be used. In case of an extensive lesion, possible spread to the regional lymph nodes must be excluded. A pre-operative scan will be required.
Plastic surgeons well trained in Dermatosurgery will be able to manage skin cancers as well as other pre-cancerous skin lesions too.